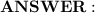
527.4 N
To find the tension in each of the cables, we'll use the concept of equilibrium. Since the loudspeaker is not accelerating vertically, the sum of the vertical forces must be zero.
Let's consider one of the cables:
The vertical components of the tensions in the cables will balance the weight of the loudspeaker.
The weight of the loudspeaker can be calculated using the formula:
Weight = mass * gravity
where mass is the mass of the loudspeaker (23.0 kg) and gravity is the acceleration due to gravity (9.80 m/s^2).
Weight = 23.0 kg * 9.80 m/s^2 = 225.4 N
Now, let's calculate the vertical components of the tensions in the cables:
The vertical component of each tension can be found using the formula:
Vertical Component of Tension = T * sin(angle)
where T is the tension in the cable and angle is the angle between the cable and the vertical direction.
Since the two cables make equal angles with the ceiling, each angle is the same. Let's call it θ.
Now, using trigonometry, we can determine θ:
sin(θ) = h / l
where h is the distance between the loudspeaker and the ceiling (1.20 m) and l is the length of each cable (2.90 m).
sin(θ) = 1.20 m / 2.90 m = 0.4138
To find θ, we take the inverse sine (sin^(-1)) of 0.4138:
θ ≈ sin^(-1)(0.4138) ≈ 24.61°
Now, we can calculate the tension in each cable:
Vertical Component of Tension = T * sin(θ)
225.4 N = T * sin(24.61°)
Divide both sides by sin(24.61°):
T ≈ 225.4 N / sin(24.61°) ≈ 527.4 N
Therefore, the tension in each of the cables is approximately 527.4 N.