Final Answer:
The stopping potential for emitted electrons when the photoelectrode is exposed to radiation of frequency 1200 THz is \( V = 3.18 \, V \).
Step-by-step explanation:
When light falls on a photoelectric material, electrons are emitted with kinetic energy determined by the energy of the incident photons. The stopping potential
 is the minimum potential that must be applied to prevent these emitted electrons from reaching the anode. The relationship between the stopping potential, frequency of incident light (\( f \)), and Planck's constant
is the minimum potential that must be applied to prevent these emitted electrons from reaching the anode. The relationship between the stopping potential, frequency of incident light (\( f \)), and Planck's constant
 is given by the equation
is given by the equation
 the elementary charge.
the elementary charge.
In this case, the frequency of the incident radiation is given as 1200 THz. To find the stopping potential, we use the formula
 Substituting the known values, with Planck's constant
Substituting the known values, with Planck's constant
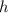 being approximately
being approximately
 and the elementary charge
and the elementary charge
 we get
we get

Solving this expression yields
 . This means that a potential of 3.18 volts must be applied to stop the emitted electrons and collect them at the anode. The stopping potential is a crucial parameter in understanding the photoelectric effect, providing insights into the energy distribution of emitted electrons and confirming the quantized nature of light.
. This means that a potential of 3.18 volts must be applied to stop the emitted electrons and collect them at the anode. The stopping potential is a crucial parameter in understanding the photoelectric effect, providing insights into the energy distribution of emitted electrons and confirming the quantized nature of light.