Based on the calculations:
- Option A is correct.
- Option B is incorrect.
- Option C is incorrect.
- Option D is incorrect, as it doesn't match any arithmetic combination of
 and
and
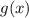 .
.
The image shows two functions,
 and
and
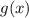 , and four arithmetic combinations of these functions. We'll need to verify each combination by performing the arithmetic operations step by step.
, and four arithmetic combinations of these functions. We'll need to verify each combination by performing the arithmetic operations step by step.
Given:
![\[ f(x) = 2x^2 + 5x - 12 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/kg872drsi4wibkzhlhn9vy7w25jzhb3t2i.png)
![\[ g(x) = 2x - 3 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/2ou9bo4goqacsvzw04jfvifmt9iavg2s5m.png)
We need to check the following combinations:
A.

B.

C.

D.

Let's perform these operations. We'll start with option A, then proceed to B, C, and D.
Let's review the calculations for each arithmetic combination:
A. For
 :
:
![\[ f(x) + g(x) = (2x^2 + 5x - 12) + (2x - 3) = 2x^2 + 7x - 15 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/zjcwsoyfyo92tvr9iyoxwylgjiqr11og9i.png)
So, option A is correct.
B. For
 :
:
![\[ f(x) - g(x) = (2x^2 + 5x - 12) - (2x - 3) = 2x^2 + 3x - 9 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/xodimcushx6vmr8jlmcxdv4dnx2pqf5q7h.png)
This does not match option B, which states
 , so option B is incorrect.
, so option B is incorrect.
C. For
 , I have the simplified expression:
, I have the simplified expression:
![\[ f(x) \cdot g(x) = (2x - 3) \cdot (2x^2 + 5x - 12) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/qaekv55bff1i67p4bfjhr6w1k9xld3g1yx.png)
This needs to be expanded to verify if it matches the given option C.
D. Option D is not a valid arithmetic combination based on the given functions and is incorrect.
Let's now expand the expression for
 to check against option C.
to check against option C.
Upon expanding
 , we get:
, we get:
![\[ f(x) \cdot g(x) = 4x^3 + 4x^2 - 39x + 36 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/i4rtdoc0obk7n9zlf0fu4lfo5tisj8bhqr.png)
This does not match option C, which states
 . Therefore, option C is incorrect.
. Therefore, option C is incorrect.
Based on the calculations:
- Option A is correct.
- Option B is incorrect.
- Option C is incorrect.
- Option D is incorrect, as it doesn't match any arithmetic combination of
 and
and
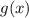 .
.
the complete Question is given below:
![\[ f(x) = 2x^2 + 5x - 12 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/kg872drsi4wibkzhlhn9vy7w25jzhb3t2i.png)
![\[ g(x) = 2x - 3 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/2ou9bo4goqacsvzw04jfvifmt9iavg2s5m.png)
Choose all arithmetic combinations that are correct
A.

B.

C.

D.
