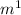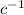Final answer:
The initial velocity at a substrate concentration of 6 µM is 0.75 µM/sec. The specificity constant for this enzyme, given the total enzyme concentration of 8 µM, is 0.025 µ
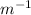
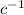
Step-by-step explanation:
The initial velocity (v) of an enzyme reaction at a given substrate concentration ([S]) when following Michaelis-Menten kinetics can be calculated using the Michaelis-Menten equation:
v = (Vmax * [S]) / (Km + [S])
Given a Km of 10 µM, a Vmax of 2 µM/sec, and a substrate concentration [S] of 6 µM, the initial velocity v is:
v = (2*6) / (10+6) = 12 / 16 = 0.75 µM/sec
The specificity constant (kcat/Km), which measures enzyme efficiency, can be calculated when the total enzyme concentration ([E]) is known and is used to find the turnover number (kcat, the number of substrate molecules converted to product per enzyme molecule per second).
kcat = Vmax / [E]
Here, [E] is 8 µM, so:
kcat = 2 / 8 = 0.25
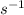
Therefore, the specificity constant is:
kcat/Km = 0.25 / 10 = 0.025 µ