Answer:
See the explanation below.
Step-by-step explanation:
By means of Hooke's second law, we can calculate the spring constant with the initial conditions of the problem.
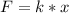
where:
k = spring constant [N/m]
x = distance = 0.01 [m]
F = force or weight [N]
Weight can be calculated by means of the product of mass by gravitational acceleration.
m = mass = 500[g] = 0.5[kg]
![W=F=m*g\\W = 0.5*9.81\\W= 4.905[N]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/physics/high-school/h4i2pxdnzzfmt6ged9rep295wy1ce0duz1.png)
Now the spring constant can be calculated:
![k=F/x\\k=4.905/0.01\\k = 490.5[N/m]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/physics/high-school/tc6l3qefnsai7p1vtllupfhxs2ppgaxsws.png)
We must now use the same Hooke's law to determine the new spring force when stretching it 0.03 [m]
![F_(new)=k*x\\F_(new)=490.5*0.03\\F_(new)=14.715[N]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/physics/high-school/c39b2tcv7tzcc50yrip56dk9wm9h7hl1cd.png)
Now we have to use Newton's second law to calculate acceleration. We must remember that Newton's Second Law tells us that the sum of forces is equal to the product of mass by acceleration.
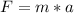
where:
F = Fnew = 14.715[N]
m = mass = 500 [g] = 0.5 [kg]
a = acceleration [m/s²]
Now replacing:
![14.715=0.5*a\\a=14.715/0.5\\a=29.43[m/s^(2) ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/physics/high-school/8ouhvz2fil4w9mzafy6oh5faeljb45tqqk.png)