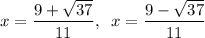Answer:
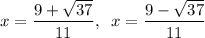
Explanation:
Given equation:
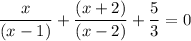
As the denominators of the fractions are different, we need to make them the same by finding the least common denominator.
The least common denominator is the product of all three denominators:
Rewrite the equation so that the denominators are the same:
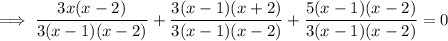
Simplify:
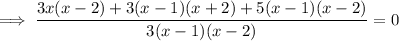
Multiply both sides by 3(x - 1)(x - 2) to eliminate the denominator:
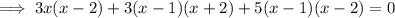
Expand:
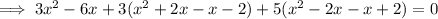
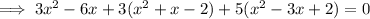
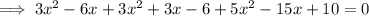
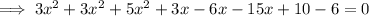
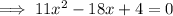
Use the quadratic formula to solve the equation.
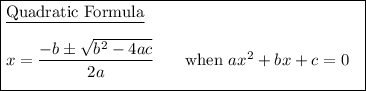
Therefore:
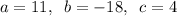
Substitute the values of a, b and c into the quadratic formula and solve for x:
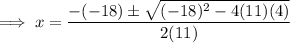
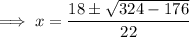
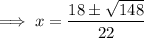
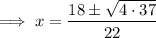
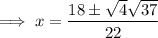
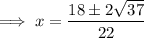
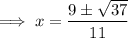
Therefore, the solutions of the equation are: