Answer:

Explanation:

Therefore:


The tan trigonometric ratio is the ratio of the side opposite the angle to the side adjacent the angle of a right triangle. Therefore, O = 5 and A = 12. Calculate the hypotenuse (H) by using Pythagoras Theorem.
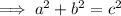




Therefore, the values are:
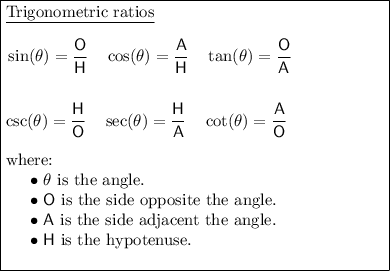
Substitute the values into the sin, cos, sec and cosec ratios then take their inverses.




Therefore, from the given answer options:
