Final answer:
To find the ratio of the mass of oxygen in the Earth's atmosphere to that in the crust, we calculate the masses of the crust and atmospheric layers considering their volumes and densities, then account for the proportion of oxygen in albite and atmospheric gases.
Step-by-step explanation:
Ratio of the Mass of Oxygen in Earth's Crust vs. Atmosphere
To calculate the ratio of the mass of oxygen in the Earth's atmosphere compared to that in the Earth's crust, we need to apply a mathematical approach to the given data. The mass of a cylindrical shell of the Earth's crust can be found using the formula for the volume of a sphere (V = ⅔3π
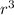 ) and subtracting the inner spherical volume from the outer to get a shell volume, and then multiplying by the density of albite. Similarly, the mass of the atmospheric shell can be calculated using the same shell volume formula and multiplying by the density of the atmosphere.
) and subtracting the inner spherical volume from the outer to get a shell volume, and then multiplying by the density of albite. Similarly, the mass of the atmospheric shell can be calculated using the same shell volume formula and multiplying by the density of the atmosphere.
Once we have these masses, we then find the percentage of oxygen in each material - albite in the crust and atmospheric compounds - and multiply this by the total masses to get the mass of oxygen in both. Finally, the ratio is the mass of atmospheric oxygen divided by the mass of crustal oxygen. Based on the provided data, the mass of crustal oxygen is quite higher than that in the atmosphere due to the large volume and high percentage of oxygen in silicates like albite.