Given:
The number of moles in gas A is,
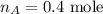
The volume of gas A is,
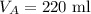
The volume of gas B is,
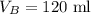
To find:
The number of moles of gas in the container that holds them B
Step-by-step explanation:
According to the ideal gas equation, as the constant temperature and pressure are constant,
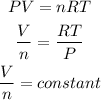
So, we write,
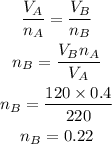
Hence, the number of moles of gas in container B is 0.22.