Let's start with the x -intercepts. The x - intercepts are the points for which y = 0, that is, f(x) = 0:
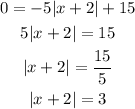
Since the module of x + 2 is 3, the inside can be either equal to 3 or -3, so:
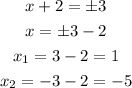
Thus, the x-intercepts are at x = 1 and x = -5 and, because they intercept x, y = 0, s they are (1, 0) and (-5, 0).
The y - intercept is the value where x = 0, so we can substitute that and sse the value of y, that is, f(0):
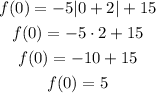
So, the y-intercept is y = 5, and because it is at x = 0, the point is (0, 5).