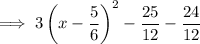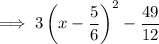Answer:
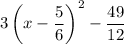
Explanation:
Given quadratic expression:
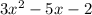
To complete the square, factor out the coefficient of the leading term:
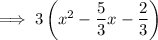
Add and subtract the square of half the coefficient of the term in x inside the parentheses:
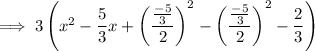
Simplify:
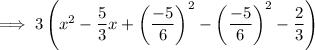
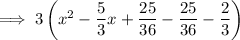
Factor the perfect square trinomial formed by the first three terms inside the parentheses:
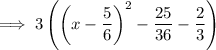
Distribute:
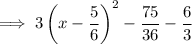
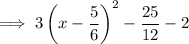
Simplify: