Answer:
See below
Explanation:
The roots aka solutions to a quadratic equation in standard form:
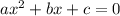
are given by
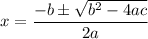
The term under the square root sign,
 is called the discriminant
is called the discriminant
The type and number of roots are determined by the sign of the discriminant
When
 there is one real root.
there is one real root.
When
 there are two real roots.
there are two real roots.
When
 there are two complex(imaginary) roots.
there are two complex(imaginary) roots.