Answer:
 to the left.
to the left.
Step-by-step explanation:
When an object of mass
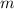 travels at a velocity of
travels at a velocity of
 , the momentum of that object would be
, the momentum of that object would be
 . Note that since velocity is a vector quantity (has a direction) while mass is a scalar, the direction of momentum would be the same as that of velocity.
. Note that since velocity is a vector quantity (has a direction) while mass is a scalar, the direction of momentum would be the same as that of velocity.
Before the collision:
- Momentum of the blue marble:
 to the left.
to the left. - Momentum of the red marble would be
 since velocity was
since velocity was
 .
.
Immediately after the collision:
- Momentum of the blue marble would be
 .
. - The momentum of the red marble needs to be found.
Momentum is conserved immediately before and after the collision. In other words, the total momentum immediately after the collision would be the same as that immediately before the collision.
In this example, total momentum was
 to the left immediately before the collision. Hence, the total momentum immediately after the collision would also be
to the left immediately before the collision. Hence, the total momentum immediately after the collision would also be
 to the left.
to the left.
Subtract the momentum of the blue marble (
 ) from the total momentum to find the momentum of the red marble:
) from the total momentum to find the momentum of the red marble:
 .
.
Divide momentum by mass to find velocity:
 .
.
Therefore, the velocity of the red marble would be
 to the left immediately after the collision.
to the left immediately after the collision.