The Pythagorean theorem states:
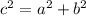
where a and b are the legs and c is the hypotenuse of a right triangle.
Substituting with b = 5, and c = 5√3, and solving for a (opposite side to angle A):
![\begin{gathered} (5\sqrt[]{3})^2=a^2+5^2 \\ 5^2(\sqrt[]{3})^2=a^2+25 \\ 25\cdot3=a^2+25 \\ 75-25=a^2 \\ \sqrt[]{50}=a \\ \sqrt[]{25}\cdot\sqrt[]{2}=a \\ 5\sqrt[]{2}=a \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/8rucw6bgf1mxk069a8ek.png)
By definition:
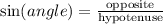
Considering angle A, the opposite side is 5√2 and the hypotenuse is 5√3. Substituting with this information, we get:
![\begin{gathered} \sin A=\frac{5\sqrt[]{2}}{5\sqrt[]{3}} \\ \sin A=\frac{\sqrt[]{2}}{\sqrt[]{3}}\cdot\frac{\sqrt[]{3}}{\sqrt[]{3}} \\ \sin A=\frac{\sqrt[]{2\cdot3}}{(\sqrt[]{3})^2} \\ \sin A=\frac{\sqrt[]{6}}{3} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/h6ygkmxbx0823twoxmud.png)
Considering angle B, the opposite side is 5 and the hypotenuse is 5√3. Substituting with this information, we get:
![\begin{gathered} \sin B=\frac{5}{5\sqrt[]{3}} \\ \sin B=\frac{1}{\sqrt[]{3}}\cdot\frac{\sqrt[]{3}}{\sqrt[]{3}} \\ \sin B=\frac{\sqrt[]{3}}{3} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/msk6x9aurwbmwrpc42oq.png)
By definition:
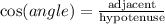
Considering angle A, the adjacent side is 5 and the hypotenuse is 5√3. Substituting with this information, we get:
![\cos A=\frac{5}{5\sqrt[]{3}}=\frac{\sqrt[]{3}}{3}](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/92e43wg1pbuq0984ee5r.png)
Considering angle B, the adjacent side is 5√2 and the hypotenuse is 5√3. Substituting with this information, we get:
![\cos B=\frac{5\sqrt[]{2}}{5\sqrt[]{3}}=\frac{\sqrt[]{6}}{3}](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/zsv9knx9a1g6sclvtjes.png)