Answer:
(a)0.5
(b)0.499
(c)Option A
Step-by-step explanation:
The outcome of the test is given below:
Outcome 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Number of Trials 98 93 101 95 92 107 103 112 107 92
(a)The theoretical probability of getting an odd number.
The odd numbers are: 1,3,5,7,9
Number of Possible Odd Numbers =5
Total Number of Outcome = 10
Therefore, the theoretical probability of getting an odd number is:
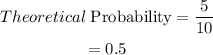
(b)Experimental probability of getting an odd number.
Total Experimental Outcomes of Odd Numbers
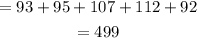
Total Number of trials =1000
Therefore, the experimental probability of getting an odd number is:
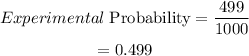
(c)
If for example, we have 2000 trials, the experimental probability of getting an odd number is:
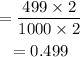
Therefore, assuming that the machine is fair, the larger the number of trials, the greater the likelihood that the experimental probability will be close to the theoretical probability.the larger the number of trials, the greater the likelihood that the experimental probability will be close to the theoretical probability.