Answer:
![f^(-1)(x)=\sqrt[4]{x}+2 \qquad \textsf{for $x \geq 0$}](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/c3cobcighm2kf2vhx9h6heg4gs2v32vgdz.png)
Explanation:
Given function:
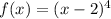
The domain of the given function is restricted:
Therefore, the range of the given function is also restricted:
To find the inverse of a function, swap x and y:
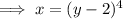
Rearrange the equation to make y the subject:
![\implies \sqrt[4]{x}=y-2](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/b4a33uwqfcni9n8ptwds47ke995o2z6jf1.png)
![\implies y=\sqrt[4]{x}+2](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/y4ioi18rq0mefj0wt0ytf6b2vnh9ub9jux.png)
Replace y with f⁻¹(x):
![\implies f^(-1)(x)=\sqrt[4]{x}+2](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/a0cy9jhori8d42riiqyxinezefqgfbf6sh.png)
The domain of the inverse of a function is the same as the range of the original function. Therefore, the domain of the inverse function is restricted to {x : x ≥ 0}.
Therefore, the inverse of the given function is:
![f^(-1)(x)=\sqrt[4]{x}+2 \qquad \textsf{for $x \geq 0$}](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/c3cobcighm2kf2vhx9h6heg4gs2v32vgdz.png)