Based on the conservation of momentum, we can determine that Car A was traveling at a speed of 31.7 mph before the collision. The speed limit is 35 mph, so Car A was not speeding at the time of the collision.
To determine whether or not Car A was speeding when it collided with Car B, we can use the following scientific explanation:
Conservation of momentum: Momentum is the product of an object's mass and velocity. In a closed system, momentum is conserved, meaning that the total momentum of all objects in the system remains constant before and after a collision.
Formula for momentum:
momentum = mass * velocity
Applying conservation of momentum to the collision of Car A and Car B:
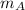 *
*
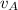 +
+
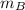 *
*
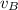 = (m_A + m_B) *
= (m_A + m_B) *
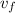
where:
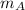 is the mass of Car A
is the mass of Car A
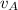 is the initial velocity of Car A
is the initial velocity of Car A
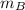 is the mass of Car B
is the mass of Car B
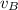 is the initial velocity of Car B
is the initial velocity of Car B
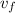 is the final velocity of both cars after the collision
is the final velocity of both cars after the collision
We know the following:
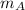 = 1550 kg
= 1550 kg
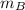 = 2100 kg
= 2100 kg
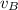 = 0 m/s (Car B was stopped at the time of the collision)
= 0 m/s (Car B was stopped at the time of the collision)
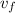 = 6.64 m/s (the final velocity of both cars after the collision)
= 6.64 m/s (the final velocity of both cars after the collision)
We can solve for
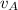 , the initial velocity of Car A:
, the initial velocity of Car A:
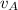 =
=
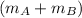 *
*
 *
*
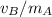
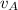 = (1550 kg + 2100 kg) * 6.64 m/s - 2100 kg * 0 m/s / 1550 kg
= (1550 kg + 2100 kg) * 6.64 m/s - 2100 kg * 0 m/s / 1550 kg
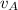 = 14.25 m/s
= 14.25 m/s
Converting
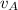 to mph:
to mph:
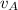 = 14.25 m/s * 2.2369 mph/m/s
= 14.25 m/s * 2.2369 mph/m/s
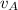 = 31.7 mph
= 31.7 mph
Based on the conservation of momentum, we can determine that Car A was traveling at a speed of 31.7 mph before the collision. The speed limit is 35 mph, so Car A was not speeding at the time of the collision.