Answer:
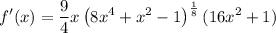
Explanation:
Given the function
![\displaystyle{f(x)=\sqrt[8]{\left(8x^4+x^2-1\right)^9}}](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/bej685z32jm622frpwi2sfov7h3simi9eq.png) . We can rewrite the function in exponential form as
. We can rewrite the function in exponential form as
 . Here, we have to know the power rules and the chain rule:
. Here, we have to know the power rules and the chain rule:
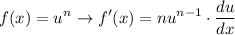
Therefore, from the above formula, we will have:
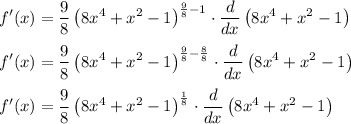
Next, we derive the function 8x⁴ + x² - 1 by applying the power rules:
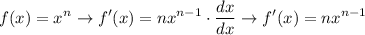
Also, deriving any constants will result in 0 always.
Therefore:
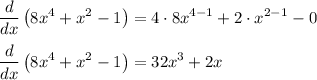
Thus, we will have:
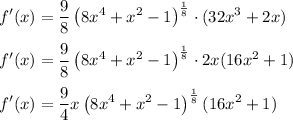
Therefore, the derivative is:
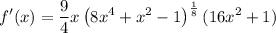
or you can rewrite in the form of surd as:
![\displaystyle{f'(x)=(9)/(4)x(16x^2+1)\sqrt[8]{8x^4+x^2-1}}](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/eqxutzmdcuy5wkast50x87hqh74tmvkdpg.png)