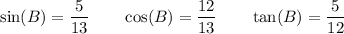Answer:
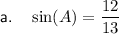
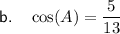
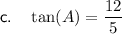
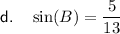
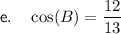
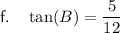
Explanation:
To find the trigonometric ratios of angles A and B in the given right triangle, we must first find the length of the hypotenuse (AB) by using Pythagoras Theorem, which states that the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the legs of a right triangle.
Therefore, the length of the hypotenuse (AB) is:
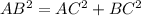
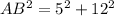
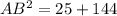
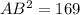
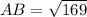
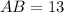
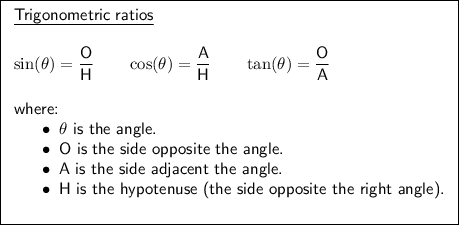
Now we have found the length of the hypotenuse of the given right triangle, we can use the following trigonometric ratios to find sin(A), cos(A), tan(A), sin(B), cos(B), and tan(B).
For angle A:
- Opposite side = 12
- Adjacent side = 5
- Hypotenuse = 13
Therefore:
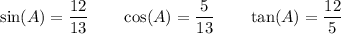
For angle B:
- Opposite side = 5
- Adjacent side = 12
- Hypotenuse = 13
Therefore: