Answer:
0.52
Step-by-step explanation:
The box is moving at constant velocity along the horizontal direction: this means that its acceleration is zero. According to Newton's second law:
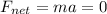
where
 is the net force acting on the object, m its mass, and a its acceleration, since the acceleration is zero, then the net force must be zero as well.
is the net force acting on the object, m its mass, and a its acceleration, since the acceleration is zero, then the net force must be zero as well.
There are in total 4 forces acting on the box:
- along the vertical direction: the weight of the box (downward), given by
 , and the normal reaction of the floor on the box (upward),
, and the normal reaction of the floor on the box (upward),
- along the horizontal direction: the force that pulls the box,
 , and the frictional force, which is given by
, and the frictional force, which is given by
 , in the opposite direction
, in the opposite direction
Since the net force is zero, the resultant on each direction must be zero. In the vertical direction we have:
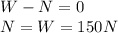
While in the horizontal direction we have
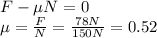
So, the coefficient of friction is 0.52.