Answer: First option is correct.
Explanation:
Since we have given that
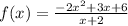
We need to find the horizontal or oblique asymptote .
Since the degree of numerator is more than the degree of denominator.
So, it has oblique asymptote.

And,
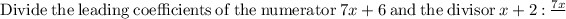
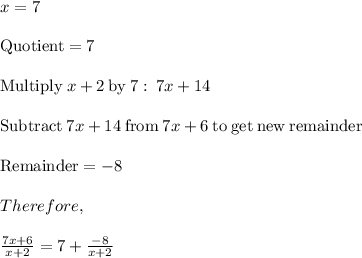
At last, we get,
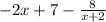
Hence, the oblique asymptote of f(x) is
y=-2x+7
Therefore, First option is correct.