Answer:
0.807g
Step-by-step explanation:
They tell us that we heat the sample and during this process its state of aggregation does not change so we are facing a sensible heat
sensible heat formula
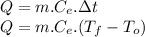
Data
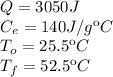
We clear the mass of the sensible heat formula
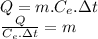
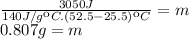
The mass of the mercury sample is 0.807g