Answer:

Step-by-step explanation:
We want to find energy and we are given the specific heat capacity, mass, and change in temperature. We must use this formula:
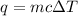
where m is mass, c is the heat capacity, and ΔT is the change in temperature.
We know the mass is 2,000 grams, the heat capacity is 3.3 J/g °C.
To find the change in temperature, subtract the final temperature and initial temperature.
- ΔT= final temp. - initial temp.
- ΔT= 55°C -25°C
- ΔT= 30°C
Substitute the known values into the formula.
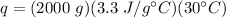
Multiply the first two numbers and note the grams will cancel out.
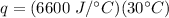
Multiply again. This time, the degrees Celsius will cancel.
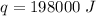
198,000 Joules of energy are required.