A second degree equation of the form
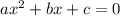
always have solutions given by
![x=\frac{-b\pm\sqrt[]{b^2-4ac}}{2a}](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/pxvjqgmokhpuiark1x2l.png)
this is called the general formula. In the general formula we have the number
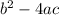
inside the squared root, this number is called the discriminant of the equation and it plays an important role in the type of solutions we'll get.
• if the discriminant is greater than zero then the equation has two real solutions.
,
• If the discrimiant is equal to zero then the equation has a real solution with multiplicity two.
,
• If the discriminant is less than zero then the equation has two complex solutions, one conjugate of the other.
For example, think of the equation
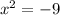
This, in standard form, is written as:
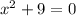
from here we see that a=1, b=0 and c=9. Then,
![\begin{gathered} x=\frac{-0\pm\sqrt[]{0^2-4(1)(9)}}{2(1)} \\ =\frac{\pm\sqrt[]{-36}}{2} \\ =\frac{\pm\sqrt[]{-9}\sqrt[]{4}}{2} \\ =(\pm2\cdot3i)/(2) \\ =\pm3i \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/8zrj9slpfgfaoxpmvs41.png)
Notice that in this case the discriminant was less than zero, then we will expect the solutions to be complex numbers.