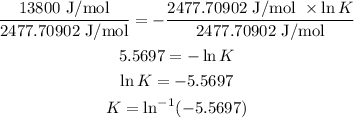Step-by-step explanation
Given:
ΔG° = 13.8 kJ/mol = (13.8 x 1000) J/mol = 13800 J/mol
Temperature, T = 25.0°C. = 25.0°C + 273 = 298.0 K
What to find:
the value of the equilibrium constant, K for the reaction at 25.0°C.
Step-by-step solution:
Both K and ΔG° can be used to predict the ratio of products to reactants at equilibrium for a given reaction.
ΔG° is related to K by the equation ΔG°= −RTlnK.
R is the molar gas constant, ( R = 8.3144598 J/K/mol)
If ΔG° < 0, then K > 1, and products are favored over reactants at equilibrium.
The next step is to substitute the values of ΔG° and T into the equation to get K.
ΔG°= −RTlnK
13800 J/mol = -(8.3144598 J/K/mol x 298 K x lnK)
13800 J/mol = -(2477.70902 J/mol x lnK)
Divide both sides by 2477.70902 J/mol