Answer : The correct option is, (a) 0.0030
Solution : Given,
Concentration of
 = 0.105 M
= 0.105 M
Concentration of
 = 1.1 M
= 1.1 M
Concentration of
 = 1.50 M
= 1.50 M
The balanced equilibrium reaction is,
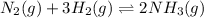
The expression for equilibrium constant of the reaction will be,
![K_(eq)=([NH_3]^2)/([N_2][H_2]^3)](https://img.qammunity.org/2017/formulas/chemistry/high-school/a0mn3p4k0rz26jxjevp276tzqcgdwfm7ys.png)
Now put all the given values in this expression, we get
![K_(eq)=([NH_3]^2)/([N_2][H_2]^3)](https://img.qammunity.org/2017/formulas/chemistry/high-school/a0mn3p4k0rz26jxjevp276tzqcgdwfm7ys.png)
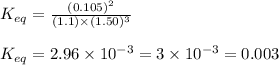
Therefore, the equilibrium constant for the reaction at this temperature will be, 0.0030