We are required to calculate the volume of O2 from the following equation:
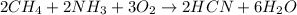
To solve this problem we have to use the ideal gas Law.
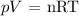
We are given the following:
V of HCN = 248 L
p = 300 kPa
T = 1200 C = 1473.15 K
We know that R = 8.314 KPa.L.K-1.mol-1
We can re-arrange the above gas law equation to find the number of moles of HCN, then we will use the stoichiometry to find the number of moles of O2, finally we can then calculate the volume using the equation.
pV = nRT
n = pV/RT
n = (300 x 248)/(8.314 x 1473.15)
n = 6.07 mol
Using the stoichiometry we know that the molar ration between HCN and O2 is 2:3
Therefore number of moles of O2:
n = 6.07 x (3/2)
n = 9.11 mole
Using the gas law we can calculate the volume of O2:
pV = nRT
V = nRT/p
V = (9.11 x 8.314 x 1473.15)/300
V = 371.92 L