Answer:
The correct option is b.
Explanation:
From the given graph it is noticed that the graph represents a parent rational function.
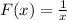
As the value of x approaches towards a small negative number.
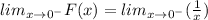
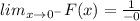
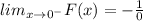
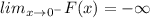
It means the value of F(x) is very large number when x is a very small negative number.
From the given graph it is clearly seen that the F(x) is very large number when x is a very small negative number.
Therefore option b is correct.