Answer: A. x = 2
Explanation:
In the given picture we have
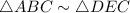
Since, we know that the corresponding sides in similar triangles are in proportion.
Therefore, we have
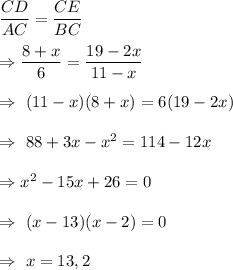
But x can not be 13 because BC=11-13=-2, which is not possible.
Therefore, the value of x=2.