Answer: 4 people can carry safely for one mission.
Explanation: To calculate the number of moles of
 produces by 1 astronaut, we use the formula:
produces by 1 astronaut, we use the formula:
 ....(1)
....(1)
Molar mass of carbon dioxide = 44 g/mol
Given mass of carbon dioxide =
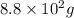
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
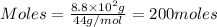
We are given a chemical equation:
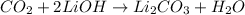
Moles of LiOH by using equation 1, we get:
Molar mass of LiOH = 24 g/mol
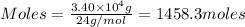
By stoichiometry of the reaction,
2 moles of LiOH produces 1 mole of

So. 1458.3 moles of LiOH will produce =
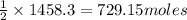 of
of

Applying Unitary method:
As, 200 moles of
 are produced by 1 astronaut
are produced by 1 astronaut
So, 729.15 moles of
 will be produced by =
will be produced by =
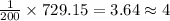 astronauts.
astronauts.