We need to calculate the heat (Q) that is absorbed by 60.5g of water evaporating from liquid to gas, and we know that this amount of water is already at its boiling temperature for 101.3kPa (that is 100°C).
So we first start by calculating how many moles of H2O we have in 60.5g. This we do by calculating the molar mass of water:
The molar mass of oxigen is 16g/mol
The molar mass of hidrogen is 1g/mol
The molar mass of water will be: 2 x 1g/mol + 16g/mol= 18g/mol
Now we calculate how many moles (n) of water we have in this sample:
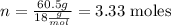
So we have 3.33 moles of water.
We know that the heat (Q) needed to evaporate the 3.33 moles of water can be calculated using the evaporation enthalpy (40.7 kJ/mol) as follows:
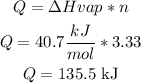
So to answer the question, the total amount of heat absorbed when 60.5g of H2O(l) at 100°C and 101.3kPa is converted to H2O(g) at 100°C and 101.3kPa is 135.5 kJ