Let us first define what the molarity of a substance corresponds to. This is defined as the moles of solute (n) per liter of solution (V), so we will have the following equation:
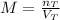
Where,
nT is the total number of moles
VT is the total volume in liters
M is the molarity of the solution
When we have a mixture we must add the total moles and the total volume as follows:
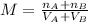
Now, the moles of each solution can be found by clearing the moles of the first equation.
But first, we have two solutions, we will call them solution a and solution b, the conditions are.
Solution a
Va=30mL=0.030L
Ma=0.100M
Solution b
Vb=10.0mL = 0.0100L
Mb=0.470M
Now for each solution, we have the following equation to find the number of moles:
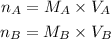
If we replace this equation into the second equation we will have:
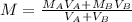
We replace the known data:
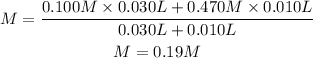
Since both ions are in the same concentration, that is to one ion per molecule, the concentration will be the same.
H+ = 0.19M
Cl- =0.19M