We can find the equivalent resistance in series as follows:
For example, let's say we have 3 resistances named R1,R2 and R3:
We can express those 3 resistances as 1 equivalent resistance as follows:
Where:
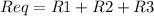
Now, you can find the voltage for each resistance as follows( Since the current is the same for a series circuit):
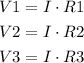
We can find the equivalent resistance in parallel using the following formula:
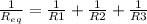
You can replace the values of each resistance and then solve for Req.
In parallel, the voltage is the same for every resistance. You need to find the total current using ohm's law:
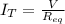
Once you find the total current, you can find the current in each resistor as follows:
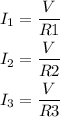
You need to compare the values you got with the values calculated in part 2. The equivalent resistance in series is higher than the equivalent resistance in parallel. Also, the current in a series circuit doesn't change but the voltage does. And the voltage in a parallel circuit doesn't change but the current does.