When gas has its molecules so far apart that there is no interaction between them, we can assume that the gas behaves like an ideal gas. The ideal gas formulation is expressed as:
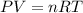
Where,
P is the pressure of the gas
V is the volume of the gas
n is the moles of the gas
R is a constant
T is the temperature of the gas
We see that this equation involves the moles of the gas, so when the gas behaves according to the ideal gas law this is the equation that is used to calculate the moles.
The other equations (Boyle's law, Charles'law, and Dalton's law) involve pressure, volume, and temperature. But they do not include moles.
So the answer will be the last option: Ideal Gas Law