1) List the known and unknown quantities.
Sample: O2.
Mass: 78.6 g.
Volume: 40.6 L.
Temperature: 43.13 ºC = 316.28 K.
Sample: F2.
Mass: 67.3 g.
Volume: 40.6 L.
Temperature: 43.13 ºC = 316.28 K.
2) Find the pressure of O2.
2.1- List the known and unknown quantities.
Sample: O2.
Mass: 78.6 g.
Volume: 40.6 L.
Temperature: 43.13 ºC = 316.28 K
Ideal gas constant: 0.082057 L * atm * K^(-1) * mol^(-1).
2.2- Convert grams of O2 to moles of O2.
The molar mass of O2 is 31.9988 g/mol.
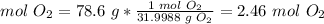
2.3- Set the equation.
Ideal gas constant: 0.082057 L * atm * K^(-1) * mol^(-1)
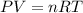
2.4- Plug in the known quantities and solve for P.
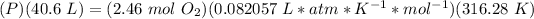
.
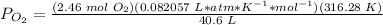
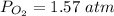
The pressure of O2 is 1.57 atm.
3) Find the pressure of F2.
3.1- List the known and unknown quantities.
Sample: F2.
Mass: 67.3 g.
Volume: 40.6 L.
Temperature: 43.13 ºC = 316.28 K.
Ideal gas constant: 0.082057 L * atm * K^(-1) * mol^(-1).
3.2- Convert grams of F2 to moles of F2.
The mmolar mass of F2 is 37.9968 g/mol.
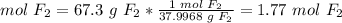
3.3- Set the equation.
Ideal gas constant: 0.082057 L * atm * K^(-1) * mol^(-1)
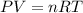
3.4- Plug in the known quantities and solve for P.
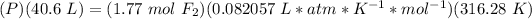
.
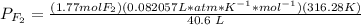
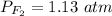
The pressure of F2 is 1.13 atm.
4) The total pressure.
Dalton's law - Partial pressure. This law states that the total pressure of a gas is equal to the sum of the individual partial pressures.
4.1- Set the equation.
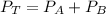
4.2- Plug in the known quantities.
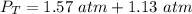
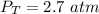
The total pressure in the container is 2.7 atm.