Answer:
v = 8.1 m/s
θ = -36.4º (36.4º South of East).
Step-by-step explanation:
- Assuming no external forces acting during the collision (due to the infinitesimal collision time) total momentum must be conserved.
- Since momentum is a vector, if we project it along two axes perpendicular each other, like the N-S axis (y-axis, positive aiming to the north) and W-E axis (x-axis, positive aiming to the east), momentum must be conserved for these components also.
- Since the collision is inelastic, we can write these two equations for the momentum conservation, for the x- and the y-axes:
- We can go with the x-axis first:
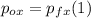
⇒
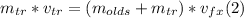
- Replacing by the givens, we can find vfx as follows:
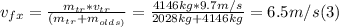
- We can repeat the process for the y-axis:
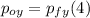
⇒
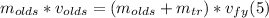
- Replacing by the givens, we can find vfy as follows:
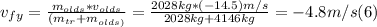
- The magnitude of the velocity vector of the wreckage immediately after the impact, can be found applying the Pythagorean Theorem to vfx and vfy, as follows:
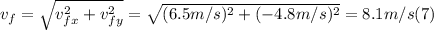
- In order to get the compass heading, we can apply the definition of tangent, as follows:
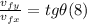
⇒ tg θ = vfy/vfx = (-4.8m/s) / (6.5m/s) = -0.738 (9)
⇒ θ = tg⁻¹ (-0.738) = -36.4º
- Since it's negative, it's counted clockwise from the positive x-axis, so this means that it's 36.4º South of East.