ANSWER:
The correct answer is 2nd option: The mass of cube A and the distance cube A falls to reach the floor
Explanation:
Final velocity for cube A after reaching on floor its equal to 0 (v = 0)
The change in potential energy provides kinetic energy for the motion of cube B, therefore:
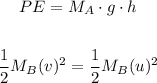
The value of v as mentioned above is equal to 0, therefore we must calculate the value u, using the following formula:
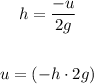
So we would finally be left with the following equation:
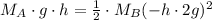
This means that if we know the mass of A and the distance cube A falls to reach the floor, we can calculate the mass of cube B.
The correct answer is 2nd option: The mass of cube A and the distance cube A falls to reach the floor