Answer:
1.62
Step-by-step explanation:
From the given information:
number of moles of benzamide
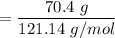
= 0.58 mole
The molality =
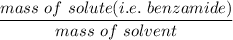
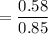
= 0.6837
Using the formula:

where;
dT = freezing point = 27
l = Van't Hoff factor = 1
kf = freezing constant of the solvent
∴
2.7 °C = 1 × kf × 0.6837 m
kf = 2.7 °C/ 0.6837m
kf = 3.949 °C/m
number of moles of NH4Cl =
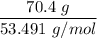
= 1.316 mol
The molality =
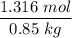
= 1.5484
Thus;
the above kf value is used in determining the Van't Hoff factor for NH4Cl
i.e.
9.9 = l × 3.949 × 1.5484 m
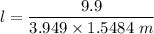
l = 1.62