Friction:
Friction is the resistive force that acts on the body in a direction opposite to the direction of motion of the same object.
Laws of friction:
1. The frictional force acting on the object is proportional to the normal force acting on the object.
For example, if the object of mass m is moving along the horizontal surface, the normal force acting on the object is mg.
Thus, the frictional force acting on the object is,
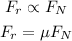
where F_N is the normal force acting on the object,
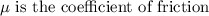
The diagrammatic representation of the frictional force acting on the object is,
2. The frictional force acting on the object depends upon the nature of the surface in contact with the object.
3. The frictional force does not depend upon the area of contact of an object with the surface.
4. The kinetic friction acting on the object is independent of the velocity of the object.
5. The coefficient of static friction is more than the coefficient of kinetic friction.
Two factors on which the frictional force depends are:
1. The frictional force depends on the adhesion between the two bodies in contact.
2. The frictional force acting on the depends upon the roughness of the surface on which the object is moving.