Answer:
The magnitude of the final speed of a raindrop by the time it reaches the ground will be 541.45 m/s.
Step-by-step explanation:
The final speed of the raindrop can be found using the following equation:
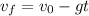
Where:
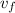 : is the final speed =?
: is the final speed =?
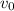 : is the initial speed
: is the initial speed
g: is the acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m/s²
t: is the time = 1.5 min
First, we need to find the initial speed:
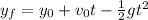
Where:
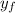 : is the final height = 0
: is the final height = 0
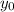 : is the initial height = 9000 m
: is the initial height = 9000 m
Hence, the initial speed is:
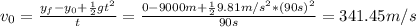
Hence, the final speed is:
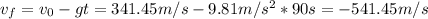
Therefore, the magnitude of the final speed of a raindrop by the time it reaches the ground will be 541.45 m/s.
I hope it helps you!