When we have an identity in algebraic terms, both sides are equal to one another.
So let's check the given equation, and expand the terms on the right side:
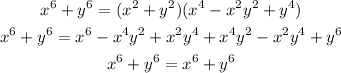
Since we could cancel out the terms in the middle, we end up as an identity for the left side is equal to the right side.
2) Therefore examining the options, we have the answer:
A)this is an identity because the equation is true