Answer:
26.2g = Mass of water in the calorimeter
Step-by-step explanation:
The heat absorbed for the water is equal to the heat released for the metal. Based on the equation:
Q = m*C*ΔT
Where Q is heat, m is the mass of the sample, C is specific heat of the material and ΔT is change in temperature
Replacing we can write:
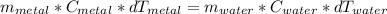
13.9g * 0.449J/g°C * (54.2°C-15.6°C) = m(H₂O) * 4.184J/g°C * (15.6°C-13.4°C)
240.9J = m(H₂O) * 9.2J/g
26.2g = Mass of water in the calorimeter