Answer:

General Formulas and Concepts:
Pre-Algebra
Order of Operations: BPEMDAS
- Brackets
- Parenthesis
- Exponents
- Multiplication
- Division
- Addition
- Subtraction
Equality Properties
Algebra I
- Functions
- Function Notation
- Exponential Rule [Multiplying]:
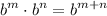
Algebra II
- Natural Logarithms ln and Euler's number e
Calculus
Derivatives
Derivative Notation
Basic Power Rule:
- f(x) = cxⁿ
- f’(x) = c·nxⁿ⁻¹
Slope Fields
- Separation of Variables
- Solving Differentials
Integrals
Integration Constant C
Integration Rule [Reverse Power Rule]:
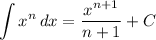
Integration Property [Multiplied Constant]:

Integration Property [Addition/Subtraction]:
![\displaystyle \int {[f(x) \pm g(x)]} \, dx = \int {f(x)} \, dx \pm \int {g(x)} \, dx](https://img.qammunity.org/2017/formulas/mathematics/high-school/9yh593om61l6o2svh84tete09z2621my15.png)
Logarithmic Integration:

Step-by-step explanation:
*Note:
When solving differential equations in slope fields, disregard the integration constant C for variable y.
Step 1: Define


Step 2: Rewrite
Separation of Variables. Get differential equation to a form where we can integrate both sides and rewrite Leibniz Notation.
- [Separation of Variables] Rewrite Leibniz Notation:

- [Separation of Variables] Isolate y's together:

Step 3: Find General Solution
- [Differential] Integrate both sides:

- [dy Integral] Integrate [Logarithmic Integration]:

- [dx Integral] Rewrite [Integration Property - Addition/Subtraction]:

- [1st dx Integral] Rewrite [Integration Property - Multiplied Constant]:

- [dx Integrals] Integrate [Integration Rule - Reverse Power Rule]:

- Simplify:

- [Equality Property] e both sides:

- Simplify:

- Rewrite:

General Solution:

Step 4: Find Particular Solution
- Substitute in function values [General Solution]:

- Simplify:

- Rewrite:

- Substitute in C [General Solution]:

- Simplify [Exponential Rule - Multiplying]:

Particular Solution:

Step 5: Solve
- Substitute in x [Particular Solution]:

- Simplify:

∴ our final answer is
 .
.
Topic: AP Calculus AB/BC (Calculus I/I + II)
Unit: Differentials and Slope Fields
Book: College Calculus 10e