Answer:
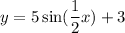
Explanation:
The Sine Function
The general form of the sine function (with no phase shift) is:
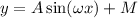
Where:
A = Amplitude
ω = angular frequency
M= Midline or vertical shift
The midline can be calculated as the mean value of the maximum and minimum values of the oscillation, thus:
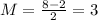
The amplitude is half the difference between the maximum and minimum values of the oscillation:
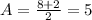
The angular frequency is calculated in terms of the period T as:
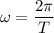
Since T=4π:
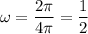
Substituting in the general form of the sine function:
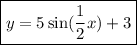
The first choice is correct