Answer:
64 g O₂
General Formulas and Concepts:
Math
Pre-Algebra
Order of Operations: BPEMDAS
- Brackets
- Parenthesis
- Exponents
- Multiplication
- Division
- Addition
- Subtraction
Chemistry
Atomic Structure
Stoichiometry
- Using Dimensional Analysis
Step-by-step explanation:
Step 1: Define
[RxN - Balanced] CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O
[Given] 36 g H₂O
[Solve] x g O₂
Step 2: Identify Conversions
[RxN] 2 mol O₂ → 2 mol H₂O
[PT] Molar Mass of O - 16.00 g/mol
[PT] Molar Mas of H - 1.01 g/mol
Molar Mass of O₂ - 2(16.00) = 32.00 g/mol
Molar Mass of H₂O - 2(1.01) + 16.00 = 18.02 g/mol
Step 3: Stoichiometry
- Set up conversion:
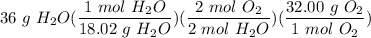
- Divide/Multiply [Cancel Units]:
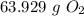
Step 4: Check
Follow sig fig rules and round. We are given 2 sig figs.
63.929 g O₂ ≈ 64 g O₂