Answer: The mole fraction of methane is 0.67 and that of propane is 0.33
Step-by-step explanation:
- The equation given by ideal gas follows:
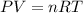
where,
P = pressure of the mixture = 1.00 atm
V = Volume of the mixture = 5.04 L
T = Temperature of the mixture =
![0^oC=[0+273]K=273K](https://img.qammunity.org/2017/formulas/chemistry/high-school/eof636bk5nddshnez1n9eet44pic938d0i.png)
R = Gas constant =
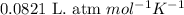
n = number of moles of mixture = ?
Putting values in above equation, we get:
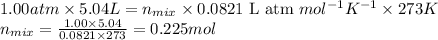
Let the number of moles of methane be 'x' moles and that of propane be 'y' moles
So,
 .....(1)
.....(1)
- The chemical equation for the combustion of methane follows:
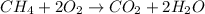
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
1 mole of methane produces 1 mole of carbon dioxide
So, 'x' moles of methane will produce =
 moles of carbon dioxide
moles of carbon dioxide
- The chemical equation for the combustion of propane follows:
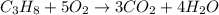
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
1 mole of propane produces 3 mole of carbon dioxide
So, 'y' moles of propane will produce =
 moles of carbon dioxide
moles of carbon dioxide
- Evaluating mass of carbon dioxide:
Total moles of carbon dioxide = (x + 3y)
Mass of carbon dioxide = (Total moles) × (Molar mass of carbon dioxide)
Molar mass of carbon dioxide = 44 g/mol
Mass of carbon dioxide =
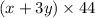
We are given:
Mass of carbon dioxide = 16.5 g
So,
 .....(2)
.....(2)
Putting value of 'x' from equation 1, in equation 2, we get:
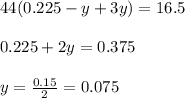
Evaluating value of 'x' from equation 1, we get:
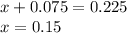
- Mole fraction of a substance is given by:
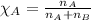
For Methane:
Moles of methane = 0.15 moles
Total moles = 0.225
Putting values in above equation, we get:
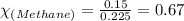
For Propane:
Moles of propane = 0.075 moles
Total moles = 0.225
Putting values in above equation, we get:
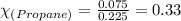
Hence, mole fraction of methane is 0.67 and that of propane is 0.33