Answer:
When we have a function like:
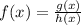
This function will have a discontinuity only if it diverges, and a divergence can happen when the denominator is equal to zero and the numerator is different than zero.
In this case, we have the equation:
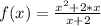
Here the denominator is:
h(x) = x + 2
This is equal to zero when:
x + 2 = 0
x = -2
Now we need to see what happens with the numerator when x = -2
g(-2) = (-2)^2 + 2*(-2) = 0
Is equal to zero.
Then we need to see the limit when x -> -2, and use the L'Hopital theorem.
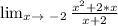
Because we have zero over zero at that point, we need to look at the quotients of the derivatives of both numerator and denominator.
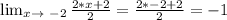
Then the function does not diverge, then the function has no discontinuity.
We also could look at the graph of f(x) to see it:
Our function is a linear function, and this is because the numerator is x times the denominator, then the function is:
f(x) = x.