In this case, we have a gas at constant pressure that varies its volume and temperature. The law that we can apply in this case is Charles's law, which relates temperature and volume while maintaining a constant pressure. Charles's law is described as:
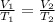
Where,
V1 is the initial volume in liters, V1=365mL=0.365L
T1 is the initial temperature in Kelvin, T1=0°C=273.15K
T2 is the final volume in Kelvin, T2=25°C=298.15K
V2 is the final volume in Liters, V2=?
Now, we clear V2 and we replace the known data:
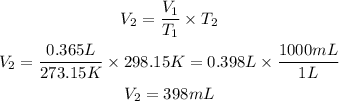
Answer: If the temperature rises to 25 degree Celsius the volume would be 398mL