Answer: 0.461 moles of

Step-by-step explanation:
According to the law of conservation of mass, mass can neither be created nor be destroyed. Thus the mass of products has to be equal to the mass of reactants. The number of atoms of each element has to be same on reactant and product side. Thus chemical equations are balanced.
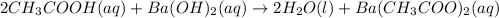
According to stoichiometry;
2 moles of
 require = 1 mole of
require = 1 mole of
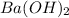
Thus 0.461 moles of
 require =
require =
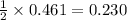 moles of
moles of
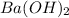
Thus 0.230 moles
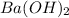 are required to completely neutralize 0.461 moles of
are required to completely neutralize 0.461 moles of
