Take into account that the magnetic force on a current line is given by:
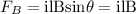
where,
i: current = ?
l: length of conductor CL = 1m
B: magnitude of magnetic field = 0.1T
θ: angle between magnetic and current vector = 90 degrees
Furthermore, by using the Newton second law, you have:
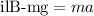
where,
m: mass of the conductor = 200g = 0.2kg
a: acceleration of the conductor
When you solve the previous equation for i, you get:
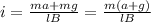
a) If the pipeline is rising at a constant speed, then a = 0m/s^2 and the current is:
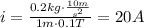
b) For a = 2 m/s^2, the current on the conductor is:
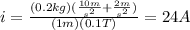
and the current flows to the right.
c) If the pipeline descends with a constant speed, then, a = 0m/s^2. The current is:
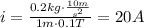
d) If the pipeline descends with a constant acceleration a = 12m/s^2, then:
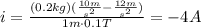
and the current flows to the left.